What makes up a motorcycle?
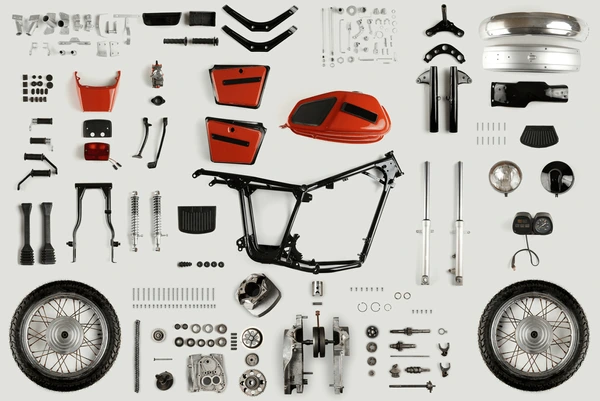

A motorcycle is a complex machine made up of various important parts, each contributing to its functionality, safety, and overall performance. Here are the key components that make up a whole motorcycle:
Frame:
The frame is the central structure of the motorcycle, providing support and connecting all the other components. It is often made of steel or aluminum and comes in different styles, such as diamond, perimeter, or trellis frames.
Engine:
The engine is the heart of the motorcycle, responsible for generating power. Motorcycles can have various types of engines, including two-stroke or four-stroke, and different configurations like inline, V-twin, or boxer engines.
Wheels:
Motorcycles typically have two wheels, one in the front and one in the rear. The wheels are crucial for stability and maneuverability. Tires provide traction and are essential for safety and handling.
Suspension:
Motorcycles have front and rear suspension systems, consisting of forks in the front and shock absorbers in the rear. These components help absorb bumps and maintain control over rough terrain.
Brakes:
Motorcycles have both front and rear brake systems. These can be disc brakes or drum brakes, and some advanced motorcycles even have ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) for added safety.
Transmission:
The transmission transfers power from the engine to the wheels. Manual motorcycles have a gearbox with multiple gears, while automatic motorcycles have a continuously variable transmission (CVT) or a dual-clutch transmission.
Exhaust System:
The exhaust system expels the exhaust gases produced by the engine. It can consist of a header pipe, muffler, and catalytic converter.
Fuel System:
This includes the fuel tank, fuel pump, and carburetor or fuel injection system, responsible for delivering fuel to the engine.
Handlebars:
Handlebars provide control over the motorcycle. The rider uses them to steer the bike and control its direction.
Seat:
The seat provides a comfortable place for the rider to sit and is usually cushioned to absorb vibrations.
Lights:
Motorcycles have front and rear lights for illumination and safety. This includes the headlight, taillight, turn signals, and brake lights.
Instrument Cluster:
The instrument cluster typically includes a speedometer, tachometer, odometer, and various indicator lights to provide the rider with important information about the motorcycle’s performance.
Controls:
The rider interacts with various controls, including the throttle, brake levers, clutch lever (if applicable), and switches for lights, horn, and other features.
Chain or Belt Drive:
Many motorcycles use a chain or belt drive to transfer power from the engine to the rear wheel. This is a critical part of the drivetrain.
Kickstand and Center Stand:
These are used to support the motorcycle when it’s parked and not in use.
Fuel and Oil Reservoirs:
These store fuel and engine oil, respectively.
Fairings and Bodywork:
Fairings are optional, but they can provide aerodynamic benefits and protection from the wind and weather. Bodywork includes the outer covering and styling elements of the motorcycle.
Conclusion
These are the essential components that make up a motorcycle. Different types of motorcycles, such as cruisers, sport bikes, touring bikes, and off-road motorcycles, may have variations and additional features to suit their specific purposes.